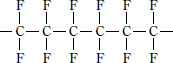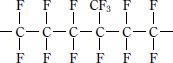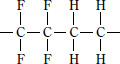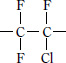Characteristics of Fluororesin
Product features
Fluororesin is a high functionality resin that has superior features in terms of heat resistance, chemical resistance, friction resistance, non-adhesion, electrical properties and the like. In recent times, it has attracted attention based on how it hardly has any outgas or extractives. It is also frequently used in fields such as semiconductors that require a clean environment. Here, we will introduce the basic characteristics of fluororesin and, in particular, the data of its characteristics that may serve as reference to you when considering the use of this resin. Additionally, the fluororesins we will mainly introduce are the PTFE and fused-type PFA(the ones that can be injection molded) that have the largest usage amounts .
(1)Type and molecular structure
(2)List of characteristics
(3)Chemical resistance
(4)Characteristics of PTFE 〈thermal expansion〉
(5)Characteristics of PTFE 〈mechanical characteristics〉
(6)Characteristics of PTFE 〈electrical characteristics〉
(7)Characteristics of PTFE 〈gas permeability〉
(8)Characteristics of PTFE 〈purity〉
(9)Characteristics of PTFE 〈purity〉
(10)Characteristics of PTFE〈non-adhesion〉
(11)Characteristics of PTFE〈noncombustibility〉
(12)Characteristics of PTFE〈radiation resistance〉
(13)Characteristics of PTFE〈adhesion〉
(14)New VALFLON
(15)PTFE containing filler〈types and features〉
(16)PTFE containing filler〈list of features〉
(17)PTFE containing filler〈list of features 2...new type〉
(18)Characteristics of PFA〈mechanical characteristics〉
(19)Characteristics of PFA〈electrical characteristics〉
■ Type and molecular structure
| Name |
Classification |
Molecular structural formula |
| PTFE |
Polytetrafluoroethylene |
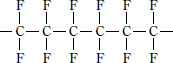 |
| PFA |
Tetrafluoroethylene-perfloroalkyl
vinyl ether copolymer resin |
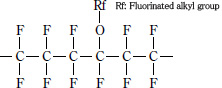 |
| FEP |
Tetrafluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene
copolymer resin |
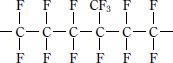 |
| ETFE |
Tetrafluoroethylene-ethylene
copolymer resin |
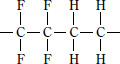 |
| CTFE |
Polytrifluorochloroethylene |
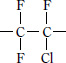 |
| PVDF |
Vinylidene fluoride resin |
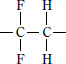 |
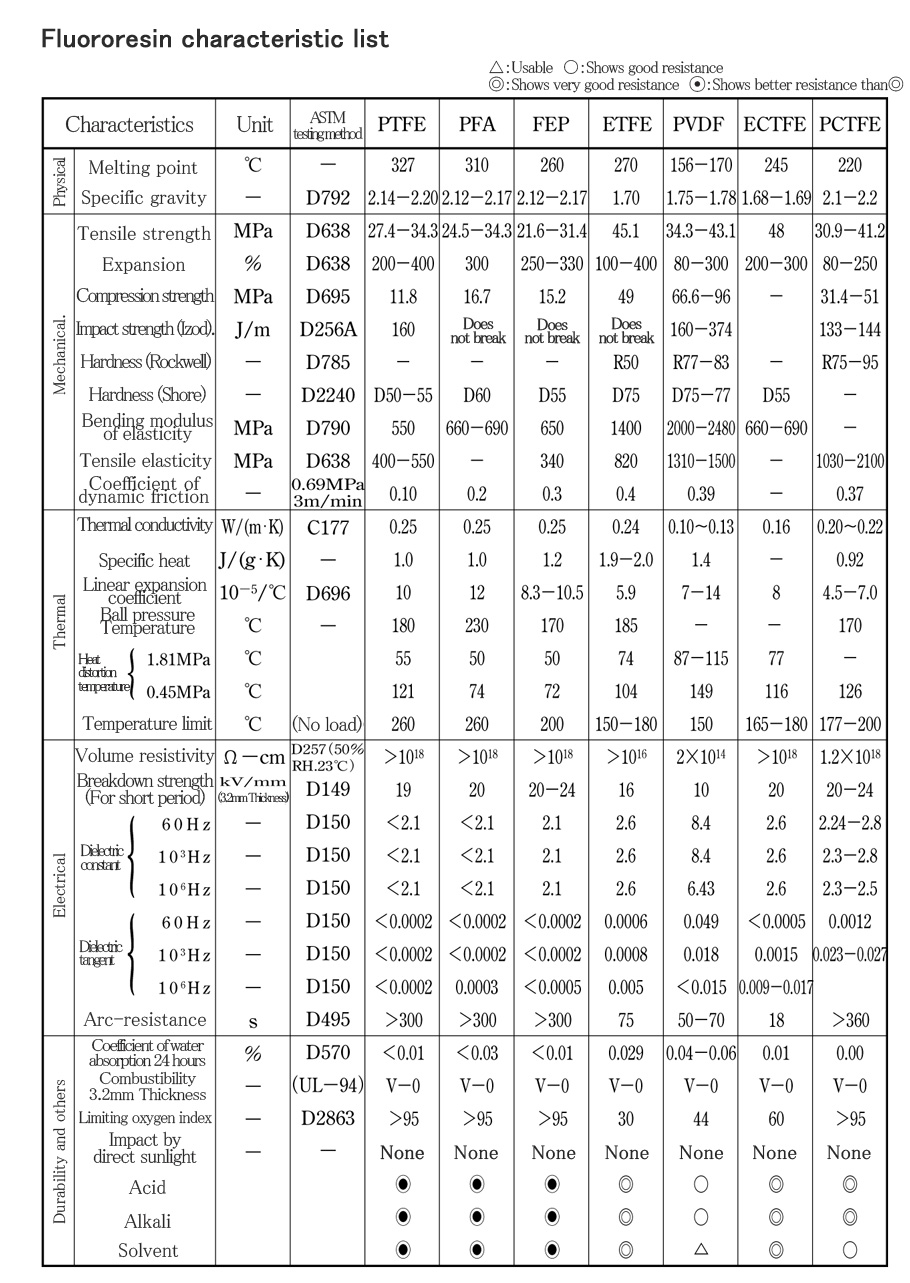
■ List of characteristics
■ Chemical resistance
Chemical resistance properties of various fluororesins
| Name |
Chemical resistance properties |
| PTFE |
This product has a very stable behavior in relation to most chemical drugs, and it is slightly affected by fused alkali metals and their liquid solutions as well as high-temperature fluorine, chlorotrifluorine and the like. |
| PFA |
Same as PTFE |
| FEP |
Same as PTFE |
| ETFE |
It is almost exactly the same as PTFE, but it is affected by concentrated nitric acid. |
| CTFE |
It is slightly inferior compared to PTFE. In addition to being affected by fused alkali metals, high-temperature fluorine and chlorotrifluorine, it is also slightly affected by chlorine gas and ammonia gas at high temperatures. Furthermore, it swells or dissolves when in contact with a special halogenated organic solvent. |
| PVDF |
It decomposes into a fuming sulfuric acid or sodium hydroxides at 100℃ or higher, and it swells or dissolves into acetone, ethyl acetate, DMF, ketone, ester, cyclic ether or amides. |
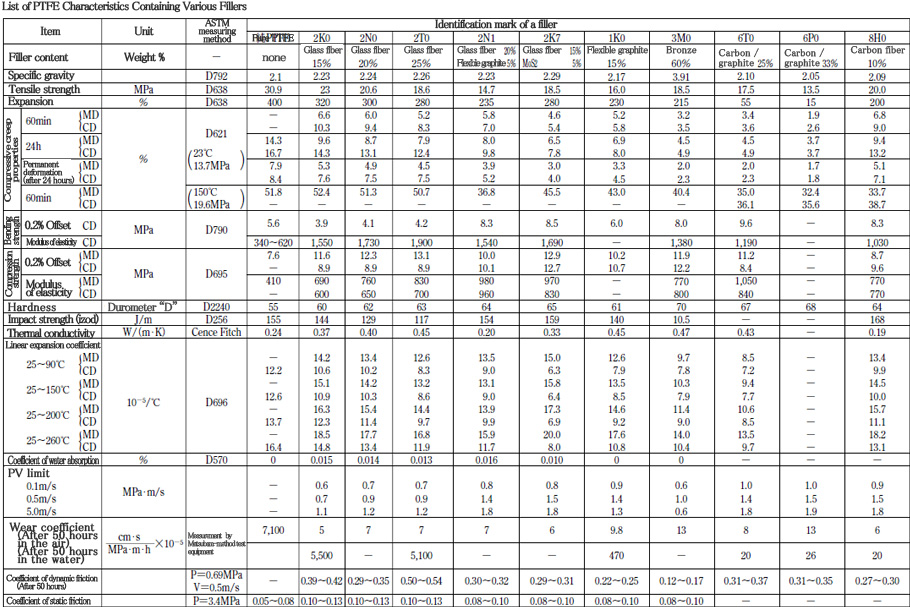
Types and features of fillers
| Types of fillers |
Identification mark of a filler |
Features |
| Glass fiber |
15%…2K0
20%…2N0
25%…2T0 |
Good wear resistance characteristics.
Good electrical characteristic.
Affected by alkali.
Weak against underwater wear. |
| Glass fiber + Flexible graphite |
20%+5%…2N1 |
Good creep-resistant characteristics.
Improves sliding characteristics. |
| Glass Fiber+MoS2 |
15%+5%…2K7 |
Good creep-resistant characteristics and compression strength.
Improves sliding characteristics.
Good electric insulation properties. |
| Flexible graphite |
15%…1K0 |
Good sliding characteristics. Does not attack soft mating materials. |
| Bronze |
60%…3M0 |
Good creep-resistant characteristics and compression strength. Good thermal conductivity. |
| Bronze + Carbon fiber |
3U8 |
Good sliding characteristics in oil. |
| Carbon graphite |
25%…6T0
33%…6P0 |
Good creep-resistant characteristics and load withstanding characteristics at high temperature. |
| Carbon fiber |
10%…8H0 |
Good sliding characteristics in water. Good creep-resistant characteristics. |
| Organic fillers |
9A1
9A2
9B1 |
Does not attack soft mating materials.
Stable sliding characteristics.
Good creep-resistant and compression characteristics. |
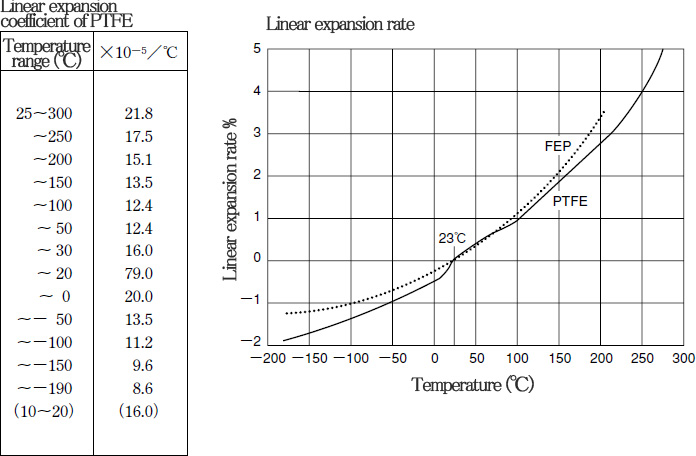
■ Characteristics of PTFE〈thermal expansion〉
PTFE demonstrates the same level of thermal expansion coefficient as general resin.
A unique transition point exists around 23℃, and special attention must be paid because a large dimensional change will take place.
■ Characteristics of PTFE〈mechanical characteristics〉
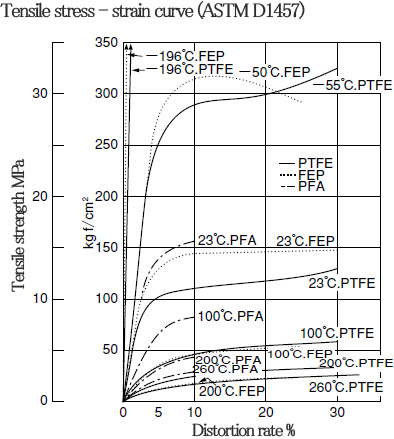
Low-temperature behaviors of PTFE, FEP and PFA
| Quality |
Temperature
(℃) |
PTFE |
FEP |
PFA |
Tensile yield point
(MPa) |
-253 |
123 |
164 |
- |
| -196 |
91 |
130 |
129 |
| -129 |
53 |
78 |
- |
| -79 |
32 |
38 |
- |
| 25 |
12 |
14 |
15 |
Tensile strength
(when rupturing)
(MPa) |
-253 |
123 |
164 |
- |
| -196 |
102 |
124 |
129 |
| -129 |
63 |
83 |
- |
| -79 |
40 |
45 |
- |
| 25 |
29 |
29 |
29 |
Tensile elasticity
(MPa) |
-253 |
4300 |
5100 |
- |
| -196 |
3200 |
4000 |
- |
| -129 |
2100 |
3300 |
- |
| -79 |
1400 |
2100 |
- |
| 25 |
600 |
500 |
- |
Expansion
(%) |
-253 |
3 |
5 |
- |
| -196 |
7 |
7 |
8 |
| -129 |
13 |
15 |
- |
| -79 |
31 |
33 |
- |
| 25 |
300 |
350 |
260 |
Bending modulus
of elasticity
(MPa) |
-253 |
5100 |
5300 |
- |
| -196 |
4700 |
4700 |
5800 |
| -129 |
3100 |
3900 |
- |
| -79 |
1600 |
2300 |
- |
| 25 |
600 |
700 |
700 |
Izod impact
strength
(Notch)(J/m) |
-253 |
75 |
98 |
- |
| -196 |
70 |
92 |
64 |
| -129 |
-80 |
- |
- |
| -79 |
|
>480 |
- |
| 25 |
101 |
Does not break |
Does not break |
Compression
strength
(MPa) |
-253 |
219 |
246 |
- |
| -196 |
145 |
206 |
412 |
| -129 |
110 |
161 |
- |
| -79 |
51 |
91 |
- |
| 25 |
26 |
11 |
25 |
Compressive
elasticity modulus
(MPa) |
-253 |
6200 |
7000 |
- |
| -196 |
5500 |
6300 |
4700 |
| -129 |
4000 |
5100 |
- |
| -79 |
2000 |
2600 |
- |
| 25 |
700 |
600 |
690 |
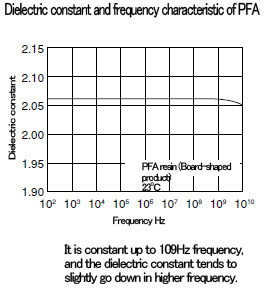
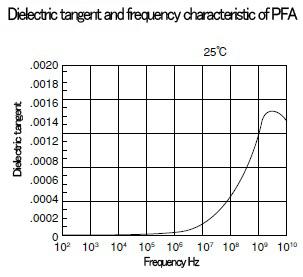
■ Characteristics of PTFE〈electrical characteristics〉
PTFE has excellent electrical characteristics.
PTFE is a resin with the smallest dielectric constant and dielectric tangent, and there is hardly any effect caused by temperature or frequency.
It has the largest insulation resistance with excellent arc-resistance.
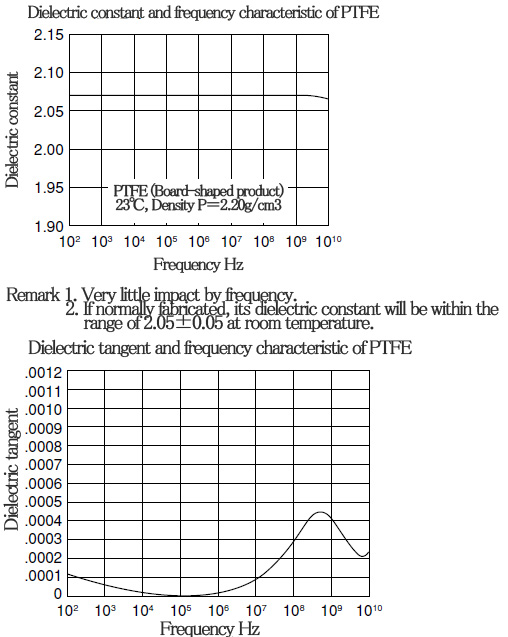
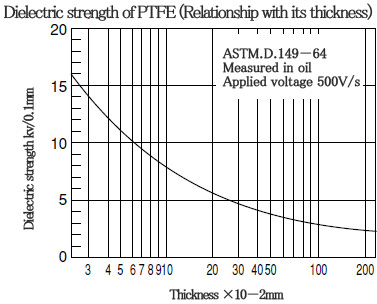
■ Characteristics of PTFE〈gas permeability〉
The gas permeation of PTFE increases together with temperature, pressure, and contact area, and it is in inverse proportion to the thickness of the film
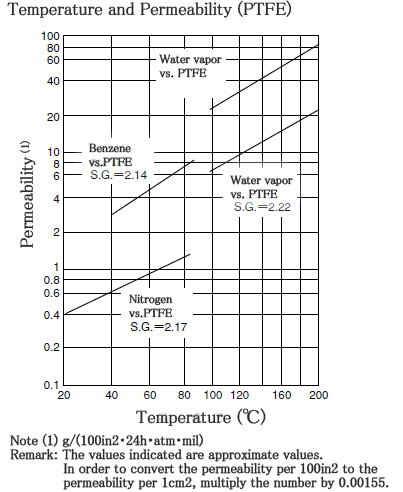
Gas transmission coefficient of PTFE film (25℃)
| O2 |
H2 |
N2 |
CO2 |
CH4 |
C2H6 |
C3H8 |
| 4.2×10-10 |
9.8×10-9 |
1.4×10-10 |
1.17×10-9 |
3.64×10-5 |
3.34×10-5 |
1.23×10-4 |
(Unit:cm3・cm・cm-2・s-1・cmHg-1)
■ Characteristics of PTFE〈purity〉
There is hardly any elution of impurities when fluororesin is in contact with a drug solution. Also, because it has superior corrosion resistance, it has an excellent characteristic in which the purity is maintained for a long time.
PTFE and PFA are types of fluororesin with particularly excellent corrosion resistance. They are frequently used in the semiconductor industry as well as microanalysis field, which require cleanliness.
The table demonstrates the nitric acid elution test results of PTFE and PFA tubes.
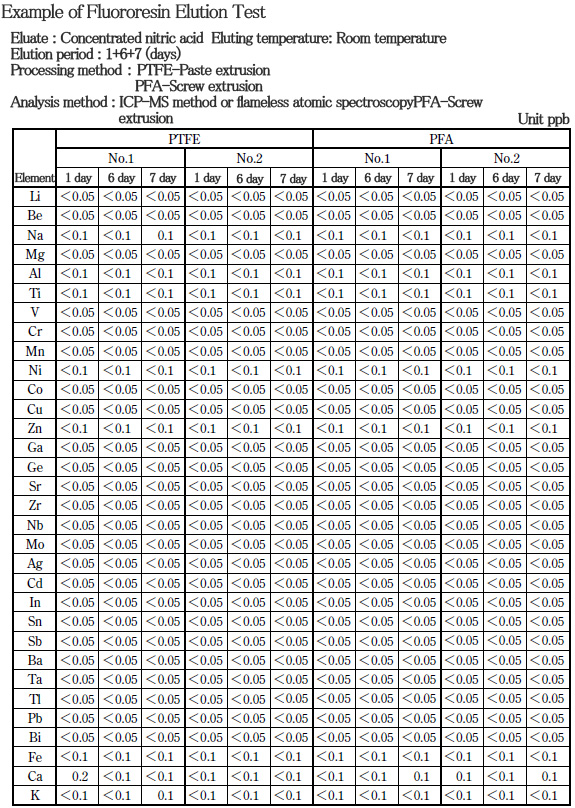
■ Characteristics of PTFE〈friction〉
PTFE is the type of resin that has the smallest coefficient of friction.
The peculiar aspect of the frictional behavior of PTFE is that a phenomenon can be seen in which the PTFE transfers to the mating material due to friction.
Once the PTFE starts to transfer to the mating material along with friction and becomes steady, then friction will occur between PTFEs, which then results in changes at low friction.
Particular attention must be paid to the large friction in a single PTFE.
Due to the large friction, a single PTFE is not practical for sliding material applications. Instead, it is used by inserting a filler and improving its wear resistance, creep resistance and other properties.
■ Characteristics of PTFE〈non-adhesion〉
Compared to other resins, PTFE, PFA and FEP have a very large contact angle and, as such, they have a characteristic of being hard to get wet.
It would therefore be extremely rare for the material in contact with the resin front surface to stick or bond.
Employing these behaviors, they are frequently used in household utensils, office equipment (e.g. fixing roll) and the like.
Wetting property
| Material type |
Water contact angle |
Adhesion energy with water |
Critical surface tension(γc) |
| (Degree) |
(×10-5N/cm) |
(×10-5N/cm) |
| FEP |
115 |
42 |
16.2 |
| PTFE |
114 |
43.1 |
18.5 |
| PFA |
(Same level as FEP and PTFE) |
| Silicone resin |
90~110 |
47.8~72.7 |
- |
| Paraffin |
10.5~10.6 |
52.7~53.8 |
23 |
| Polyethylene |
88 |
75.2 |
31 |
| Nylon |
77 |
97.7 |
46 |
| Phenol |
60 |
109 |
- |
■ Characteristics of PTFE〈noncombustibility〉
Limiting oxygen index (LOI) and combustion calorie
| |
PTFE |
ETFE |
Silicone rubber |
Vinyl chloride |
Polyethylene |
| LOI(%) |
95 or higher |
30 |
25~40 |
40 |
18 |
Combustion calorific value
(J/g) |
Approx. 4,200 |
Approx. 15,700 |
Approx. 19,000 |
Approx. 18,000 |
Approx. 46,500 |
■ Characteristics of PTFE〈radiation resistance〉
The radiation resistance of PTFE impels the cleaving reaction of molecular chains due to oxygen when in air,
and damage starts to occur between 0.2 and 0.7 x 104Gy.
The table shows the changes in mechanical strength due to radiation exposure.
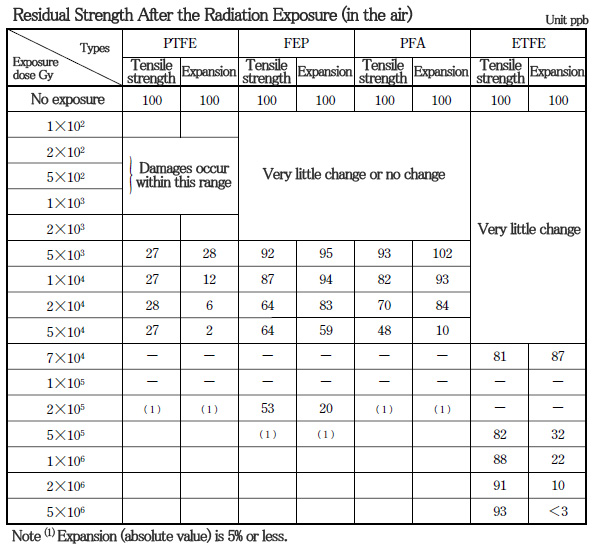
■ Characteristics of PTFE〈adhesion〉
The superior nonadhesive properties of PTFE result in the problem of being hard to stick when bonding and using in combination with other materials. In response to this problem, surface treatment is conducted as a pretreatment for adhesion.
One method of carrying out a chemical surface treatment is to use the liquid solution of alkali metal. Examples of physical surface treatment methods include the sputter etching method and plasma treatment method.
When bonding multiple PTFEs together, you can employ the fusing method that is conducted through PFA or FEP, the welding method that uses PFA beads, or other methods.
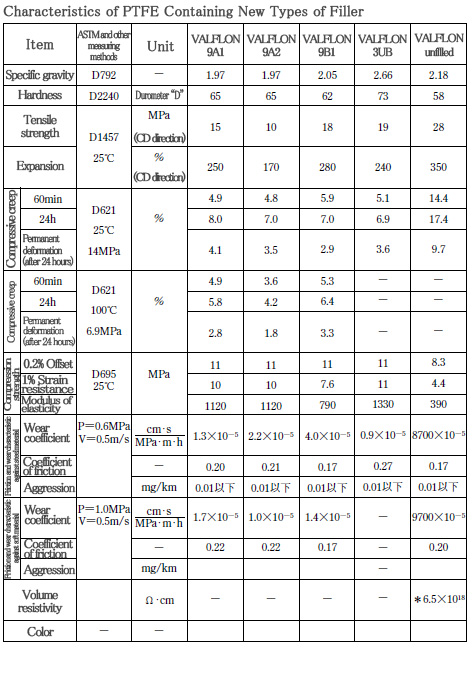
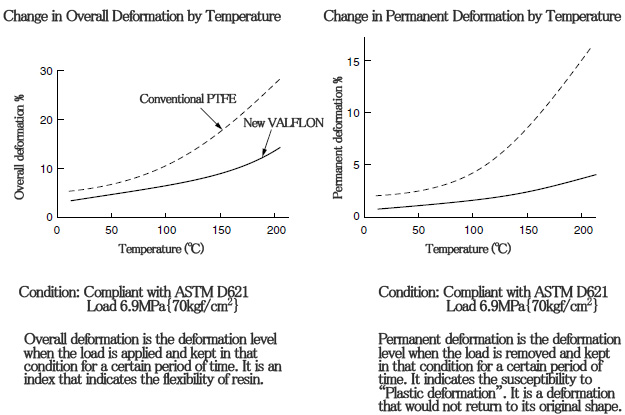
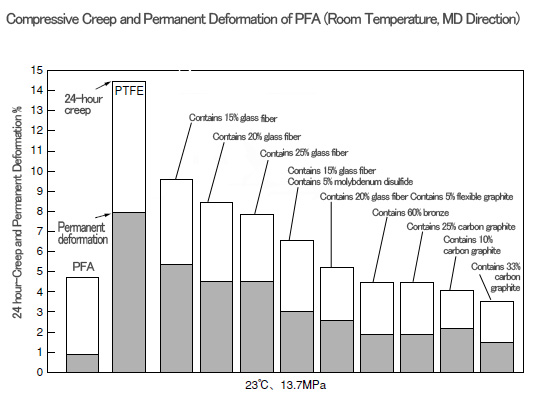
■ New VALFLON
We have developed a new type of PTFE (New VALFLON) that improves characteristics such as creep resistance, secondary processing and resistance to fatigue from flexing, while retaining the superior characteristics of conventional PTFE such as heat resistance, chemical resistance, non-adhesion and low friction.
Creep-resistant properties are shown in the figure below. Conventional PTFE had a flaw in which the creep would get larger when the temperature increased, but New VALFLON has the feature of being difficult to deform even at high temperature. As a consequence, it can obtain a higher
durability under more severe conditions than in the past in gaskets, sealing materials for automobiles, valve sheets and the like.
Additionally, in terms of resistance to fatigue from flexing, New VALFLON has been demonstrated to have a several times longer life than the conventional PTFE in a MIT test.
It can further enhance reliability in applications such as for bellows, diaphragm and sealing material.
Other features of New VALFLON that can be raised include improved electric insulation and excellent transparency.
■ PTFE containing filler〈types and features〉
Filler
Identification mark |
Main filler |
Hue |
Characteristics ◎: Excellent ○: Usable △: Usable depending on the application ×: Preferable not to use |
| Low friction quality |
Low wear quality |
Creep resistance |
Electric insulation |
Prevention of static charge |
Compression strength |
Heat resistance |
Chemicals resistance |
Machining properties |
Other features |
| Pure PTFE |
- |
Milky-white |
◎ |
△ |
△ |
◎ |
× |
× |
◎ |
◎ |
◎ |
|
| 2K0 |
Glass fiber |
White |
○ |
○ |
○ |
◎ |
× |
○ |
◎ |
○ |
○ |
Affected by alkali
Weak against underwater wear |
| 2N0 |
Glass fiber |
White |
○ |
○ |
○ |
◎ |
× |
○ |
◎ |
○ |
○ |
| 2T0 |
Glass fiber |
White |
△ |
○ |
○ |
◎ |
× |
○ |
◎ |
○ |
○ |
| 2N1 |
Glass fiber+
Flexible graphite |
Black |
○ |
○ |
◎ |
○ |
× |
○ |
◎ |
○ |
○ |
|
| 2K7 |
Glass fiber+
MoS2 |
Black |
○ |
○ |
◎ |
◎ |
× |
○ |
◎ |
△ |
○ |
|
| 1K0 |
Flexible graphite |
Black |
○ |
○ |
○ |
△ |
○ |
○ |
◎ |
○ |
○ |
Does not attack soft mating materials |
| 3M0 |
Bronze |
Loess |
○ |
○ |
◎ |
× |
○ |
○ |
◎ |
△ |
○ |
Good thermal conductivity |
| 6T0 |
Carbon graphite |
Black |
○ |
○ |
◎ |
× |
○ |
◎ |
◎ |
○ |
○ |
Good sliding characteristics in oil |
| 6P0 |
Carbon graphite |
Black |
○ |
○ |
◎ |
× |
○ |
○ |
◎ |
○ |
○ |
|
| 8H0 |
Carbon fiber |
Black |
○ |
○ |
○ |
× |
△ |
△ |
◎ |
○ |
○ |
Good sliding characteristics in water |
| 9A1 |
Organic fillers |
Pale yellow |
○ |
○ |
○ |
○ |
× |
○ |
◎ |
○ |
○ |
Does not attack soft mating materials |
| 9A2 |
Organic fillers |
Pale yellow |
○ |
○ |
○ |
○ |
× |
○ |
◎ |
○ |
○ |
Does not attack soft mating materials |
| 9B1 |
Organic fillers |
Black |
○ |
○ |
◎ |
△ |
× |
○ |
◎ |
○ |
○ |
Does not attack soft mating materials |
| 3U8 |
Bronze + Carbon fiber |
Blackish brown |
○ |
○ |
○ |
△ |
△ |
○ |
◎ |
△ |
○ |
|
| 4Y0 |
Electrically-conductive carbon |
Black |
○ |
△ |
△ |
× |
◎ |
× |
◎ |
○ |
◎ |
|
■ PTFE containing filler〈list of features〉
■ PTFE containing filler〈list of features 2...new type〉
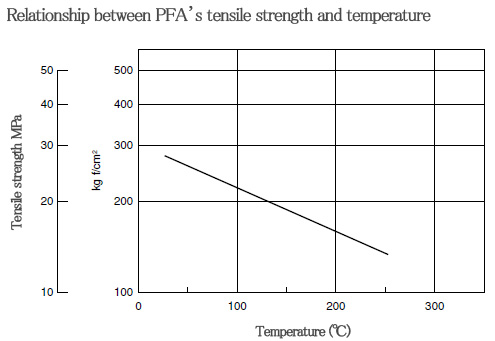
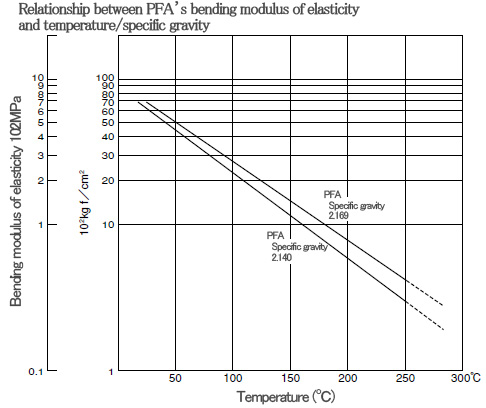
■ Characteristics of PFA〈mechanical characteristics〉
Similar to PTFE, the mechanical strength of PFA around room temperature cannot be said to be a high level, but the strength and creep resistance of PFA in high temperature areas are superior compared to PTFE.
| Features |
ASTM testing method |
Temperature ℃ |
PFA |
PTFE(1) |
FEP |
| 340-J |
350-J |
T-160 |
| Tensile strength MPa |
D 1708 |
23 |
27 |
31 |
27-34(2) |
31 |
| 250 |
12 |
14 |
10 |
2 |
| Tensile yield point MPa |
D 1708 |
23 |
14 |
15 |
10 |
14 |
| 250 |
3.4 |
4 |
2 |
1.5 |
| Expansion % |
D 1708 |
23 |
300 |
300 |
300 |
300 |
| 250 |
480 |
500 |
350 |
350 |
| Bending modulus of elasticity MPa |
D 790 |
23 |
660 |
690 |
270-620(2) |
690 |
| 250 |
55 |
70 |
27 |
21 |
■ Characteristics of PFA〈electrical characteristics〉